How Accurate Are Body Composition Scales and How Do Work?
Keeping track of health and fitness has never been easier, thanks to the advent of body composition scales. These devices promise to deliver comprehensive insights into your body's makeup, allowing for easy and convenient monitoring of changes over time. However, a crucial question arises: how accurate are these body composition scales? In this guide, we will delve into the mechanics of body composition scales, investigate their accuracy, and explore other reliable methods for measuring body fat and overall body composition. Whether you're a fitness enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or someone seeking better ways to monitor your health, this guide will provide you with essential information to understand and effectively utilize body composition scales. Let's dive in!
How do body composition scales work?
Body composition scales, also known as bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) scales, operate by measuring the resistance of body tissues to a small, safe electrical current. This process helps estimate the proportion of fat, muscle, bone, and water in your body. Here’s a detailed look at how these scales function:
1. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) Principle
Electrical Conductivity: Different body tissues conduct electricity differently. Muscle and water are good conductors because they contain high amounts of fluid and electrolytes, whereas fat and bone are poor conductors.
2. Measurement Process
Electrodes: When you step on a body composition scale, it typically has metal electrodes that come into contact with your feet. Some advanced models also have hand-held electrodes or additional sensors for more accurate readings.
Current Transmission: The scale sends a low-level electrical current through one foot, up your leg, across your pelvis, and down the other leg.
Impedance Measurement: The scale measures the impedance, or resistance, to the electrical current as it passes through your body. This impedance is influenced by the amount of water in the tissues, as water conducts electricity well.
3. Data Calculation
Impedance to Body Composition: The scale uses the measured impedance along with additional personal data inputs (age, sex, height, and weight) to estimate body composition. This calculation is based on algorithms derived from population studies that consider how electrical resistance correlates with body composition in different individuals.
Output Metrics:
- Body Fat Percentage: Proportion of your body that is fat.
- Muscle Mass: Total weight of muscle in your body.
- Bone Mass: Total weight of bone mineral in your body.
- Body Water: Total amount of water in your body.
4. Factors Affecting Accuracy
Hydration Level: Body hydration significantly affects impedance measurements. Dehydration can increase impedance, leading to higher body fat estimates, while overhydration can have the opposite effect.
Recent Food and Drink Intake: Eating or drinking before measurement can alter body water distribution and impact results.
Physical Activity: Exercise before measurement can temporarily change body water content and distribution, affecting the readings.
Body Temperature: Variations in body temperature can influence electrical impedance.
5. Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Convenience: Quick and easy to use at home.
- Non-Invasive: Safe and painless method for estimating body composition.
- Tracking Progress: Useful for monitoring changes over time when used consistently.
Limitations:
- Accuracy: BIA scales are less accurate than clinical methods like DEXA scans or hydrostatic weighing, with potential error margins of 3-5% for body fat measurements.
- Variability: Results can vary based on hydration, time of day, and recent physical activity.
How accurate are body composition scales?
Delving into the precision of body fat scales, this section meticulously examines the factors influencing their accuracy. From hydration levels to body composition, we unravel the intricacies contributing to the readings on these scales. Understanding these limitations empowers us to interpret the results more effectively.
1. Influence of Hydration Levels
The level of hydration plays a crucial role in determining the accuracy of body fat measurements on scales. These scales utilize bioelectrical impedance analysis to assess body composition, relying on the conductivity of water. Consequently, fluctuations in hydration levels can impact the reliability of readings. In cases of dehydration, the apparent body fat percentage might register higher due to decreased water content hindering the conductivity of the electrical signal.
2. Variations in Body Composition
Diverse body compositions can introduce discrepancies in the accuracy of body fat scales. While the most precise models are typically calibrated for average body types, they may not be as effective for individuals with atypical compositions. For example, those with notably higher or lower body fat percentages than the average might experience reduced reliability with these scales.
3. Muscle Mass
Muscle mass can also impact the accuracy of body fat scale readings. Since muscle conducts electrical impulses better than fat, individuals with higher muscle mass might find that their body fat percentage is underestimated. This is a common issue in athletes and bodybuilders, who may need to look for the most accurate smart scale specifically designed for their body type.
4. Age and Gender
Age and gender are important variables that body fat scales use to estimate body composition. Women naturally have a higher body fat percentage than men, and body fat tends to increase with age. While asking "Are body fat scales accurate?", it's essential to consider whether the scale adjusts for these differences effectively. The most accurate body fat scales usually allow users to input their age and gender for more tailored readings.
5. Pregnancy Considerations
During pregnancy, body composition undergoes significant changes, which can affect the accuracy of body fat scales. Pregnant women might see fluctuating or inaccurate readings due to increased body fluid and other physiological changes. It's generally advised that pregnant women avoid using these scales for body fat measurements due to these inaccuracies.
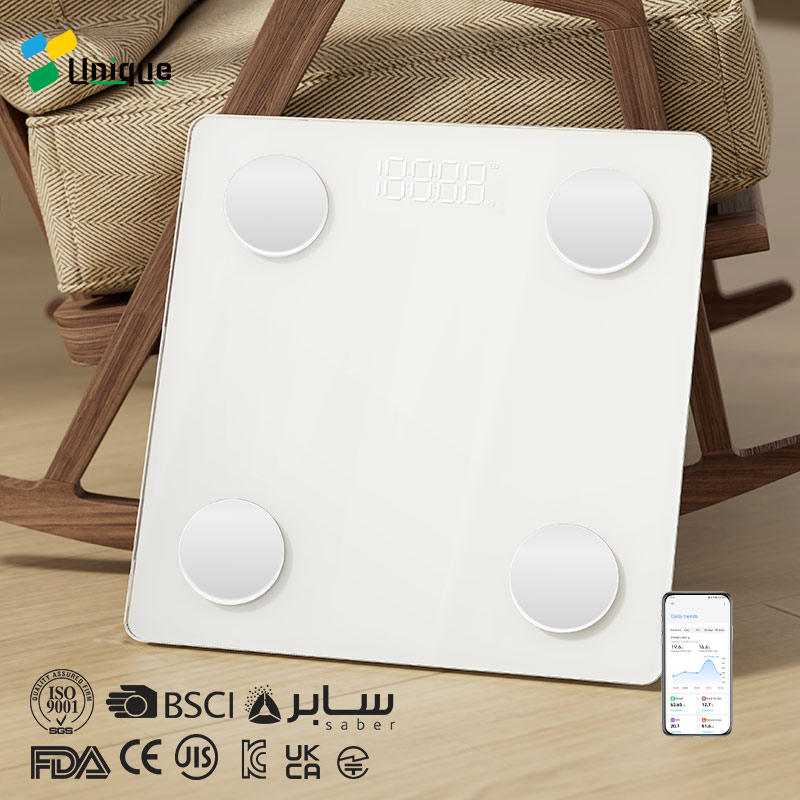
Body composition scales offer a quick and easy way to estimate body fat percentage, making them ideal for average-sized people looking for fast results but not demanding accuracy. Accuracy is guaranteed with the CF598 body composition scale, which features a sensitive ITO coating and an advanced pressure sensor that delivers up to 0.1 lbs/50 grams of accuracy, ensuring reliable weight measurements. However, for those seeking a more accurate assessment of body fat, technologies such as DEXA and hydrostatic weighing are recommended. The following sections examine these more accurate methods in more depth.

Related Reading:Other Most Accurate Ways To Measure Body Fat